Personal Finance Classes in High School: Complete Guide to Financial Education Requirements
Understand personal finance education in high schools
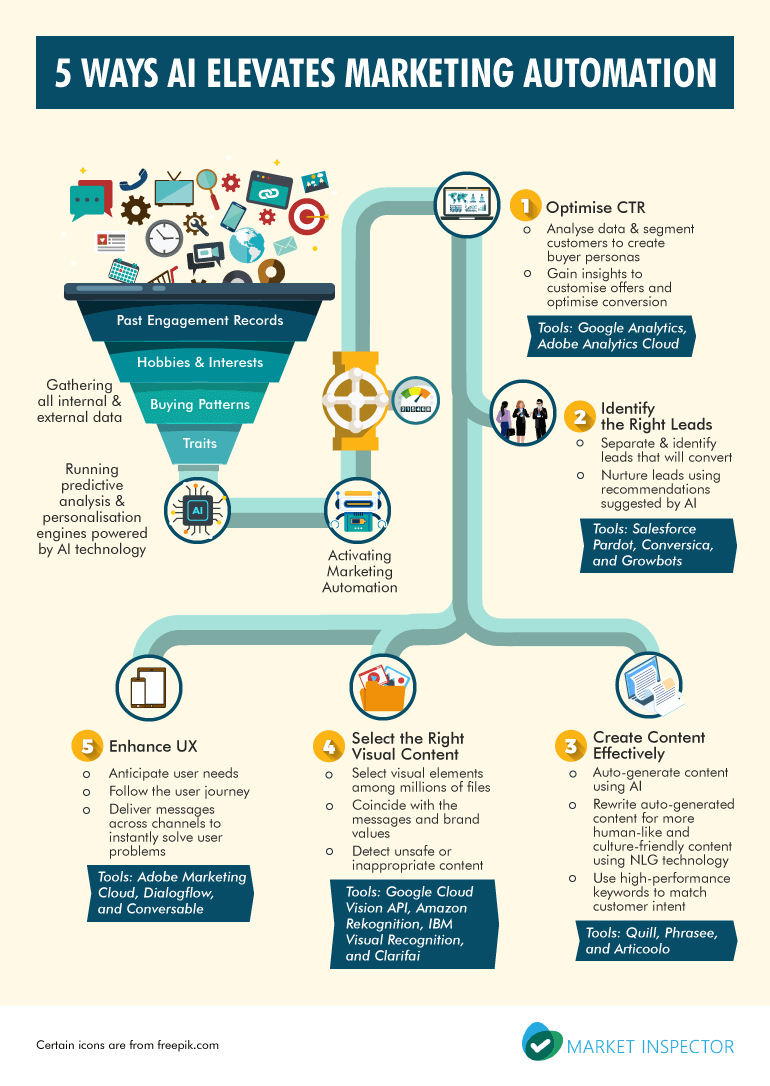
Personal finance education has become progressively important in high school curricula as educators recognize the critical need for financial literacy among young adults. Many students graduate without basic knowledge of budgeting, saving, investing, or manage debt, make personal finance classes essential preparation for adult financial responsibilities.
The structure and requirements for personal finance education vary importantly across different states and school districts. Some states mandate personal finance as a graduation requirement, while others offer it as an elective course. This variation create an uneven landscape of financial education opportunities for students nationally.

Source: financialeducatorscouncil.org
Is personal finance an elective course?
The classification of personal finance as either a requirement course or elective depend mostly on state education policies and individual school district decisions. Presently, more than half of u.s. states require high school students to take some form of personal finance education, though the implementatvariesvary substantially.
In states where personal finance is not mandated, schools typically offer these courses as electives. Students can choose to enroll base on their interest in financial topics or college and career planning needs. Notwithstanding, yet in states with requirements, some schools integrate personal finance concepts intoothersr require courses like social studies or mathematics preferably than offer standalone classes.

Source: worksheets.clip art library.com
The trend is move toward make personal finance education mandatory. States like Florida, Texas, and North Carolina have latterly strengthened their financial literacy requirements, recognize that optional courses frequently fail to reach all students who need this essential knowledge.
State by state variations
States with strong personal finance requirements typically mandate a semester long course cover comprehensive financial topics. These requirements oftentimes specify minimum instructional hours and specific learn objectives that must be meet for graduation.
In contrast, states without specific mandates may leave financial education decisions to local school districts. This approach can result in significant disparities in financial education quality and availability, flush within the same state.
What personal finance classes cover
Personal finance courses in high school provide students with practical knowledge and skills for manage money throughout their lives. The curriculum typically will cover fundamental concepts that students will encounter as they’ll transition to independence and adulthood.
Core curriculum components
Budgeting and money management form the foundation of most personal finance courses. Students learn to create and maintain budgets, track expenses, and make informed spending decisions. These skills provide the groundwork for all other financial concepts cover in the class.
Banking and financial services education help students understand different types of accounts, banking fees, and how to choose appropriate financial institutions. Students learn about checking and savings accounts, online banking, and the importance of maintain good banking relationships.
Credit and debt management represent a crucial component of personal finance education. Students explore how credit work, the importance of credit scores, and strategies for responsible borrowing. This section oftentimes include practical exercises in compare loan terms and understand the long term costs of debt.
Insurance concepts introduce students to risk management through various insurance types include auto, health, and life insurance. Students learn how insurance work, how to evaluate coverage needs, and the financial protection insurance provide.
Investment and savings strategies
Investment education cover basic concepts of save and invest for long term goals. Students learn about different investment vehicles, the power of compound interest, and retirement planning basics. Many courses include simulate investment activities to provide hands-on experience.
Career and income planning help students understand the relationship between education, career choices, and earn potential. This component oftentimes includes resume writing, job search strategies, and understand employee benefits.
Consumer awareness and protection teach students to make informed purchasing decisions, recognize scams, and understand their rights as consumers. This practical knowledge help students avoid common financial pitfalls and make better spending choices.
Benefits of high school personal finance education
Research systematically demonstrate that students who receive formal personal finance education make better financial decisions as adults. These courses provide immediate practical benefits as students begin earn income and make independent financial choices.
Students who complete personal finance courses show improve financial behaviors include higher savings rates, better credit management, and lower default rates on loans. These positive outcomes extend advantageously beyond high school graduation, influence lifelong financial success.
Personal finance education likewise helps reduce financial stress and anxiety by provide students with confidence and knowledge to handle financial challenges. Students learn problem solve skills that apply to various financial situations they may encounter throughout their lives.
College and career preparation
Personal finance courses prepare students for the financial realities of college and career transitions. Students learn about student loans, college financing options, and post graduation financial planning. This preparation help students make more inform decisions about higher education investments.
Career focus financial education help students understand salary negotiations, employee benefit evaluation, and workplace retirement plans. These skills become instantly relevant as students enter the workforce or pursue further education.
Teach methods and resources
Effective personal finance education combine theoretical knowledge with practical application. Many courses use real world simulations, case studies, and interactive activities to engage students and reinforce learn objectives.
Technology integration has enhanced personal finance education through online simulations, budgeting apps, and investment games. These tools allow students to practice financialdecision-makingg in safe, control environments before apply skills in real situations.
Guest speakers from financial institutions, investment firms, and other financial professionals oftentimes supplement classroom instruction. These experts provide current industry insights and real world perspectives that enhance textbook learn.
Assessment and evaluation
Personal finance courses typically use varied assessment methods include traditional tests, project base evaluations, and practical applications. Students might complete budgeting projects, research financial products, or develop comprehensive financial plans.
Portfolio base assessment allow students to demonstrate learn through collect work samples and reflective analysis. This approach emphasize practical application and personal relevance of financial concepts.
Challenges in personal finance education
Despite grow recognition of its importance, personal finance education face several implementation challenges. Teacher preparation and professional development represent significant obstacles, as many educators lack formal training in financial concepts.
Curriculum standardization vary wide, make it difficult to ensure consistent quality across different schools and regions. Some programs provide comprehensive, rigorous instruction while others offer solely superficial coverage of financial topics.
Student engagement can be challenging when financial concepts seem abstract or irrelevant to teenage experiences. Effective programs address this challenge by connect financial principles to students’ current lives and future goals.
Resource and funding limitations
Many schools struggle with limited resources for personal finance education include outdated textbooks, insufficient technology, and lack of specialized teaching materials. These limitations can compromise the quality and effectiveness of financial education programs.
Professional development opportunities for teachers may be limited or expensive, make it difficult for educators to stay current with financial industry changes and best teaching practices.
Future of personal finance education
The future of personal finance education look promise as more states recognize its importance and implement stronger requirements. Advocacy groups, financial institutions, and educational organizations continue push for expand financial literacy programs.
Technology will potential will play a progressively important role in personal finance education through virtual reality simulations, artificial intelligence tutoring systems, and will personalize learning platforms. These innovations could make financial education more engaging and effective.
Integration with other subjects may become more common, with financial concepts incorporate into mathematics, social studies, and career preparation courses. This interdisciplinary approach could reinforce financial learning while maximize instructional time.
Measure long term impact
Ongoing research into the long term effects of personal finance education will help will refine curriculum and teaching methods. Studies track graduates’ financial behaviors provide valuable feedback for program improvement.
Standardized assessment tools may emerge to measure financial literacy systematically across different programs and regions. These assessments could help identify effective practices and areas need improvement.
Prepare students for financial success
Personal finance education in high school serve as a crucial foundation for lifelong financial success. Whether you will offerIas a will require course or elective, these programs will provide essential knowledge and skills that students will use throughout their adult lives.
The virtually effective personal finance courses combine comprehensive curriculum coverage with practical application opportunities. Students benefit from learn environments that connect financial concepts to their personal experiences and future goals.
As financial products and services continue to evolve, personal finance education must adapt to prepare students for change economic realities. This ongoing evolution ensure that financial education remain relevant and valuable for each new generation of students.
Schools, parents, and communities all play important roles in support personal finance education. Collaborative efforts between these stakeholders can enhance the quality and impact of financial literacy programs, advantageously prepare young adults for financial independence and success.